√70以上 0.2 offset yield strength calculation 209518
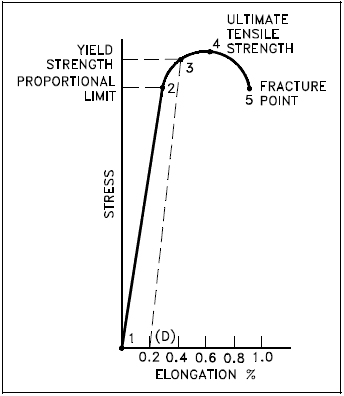
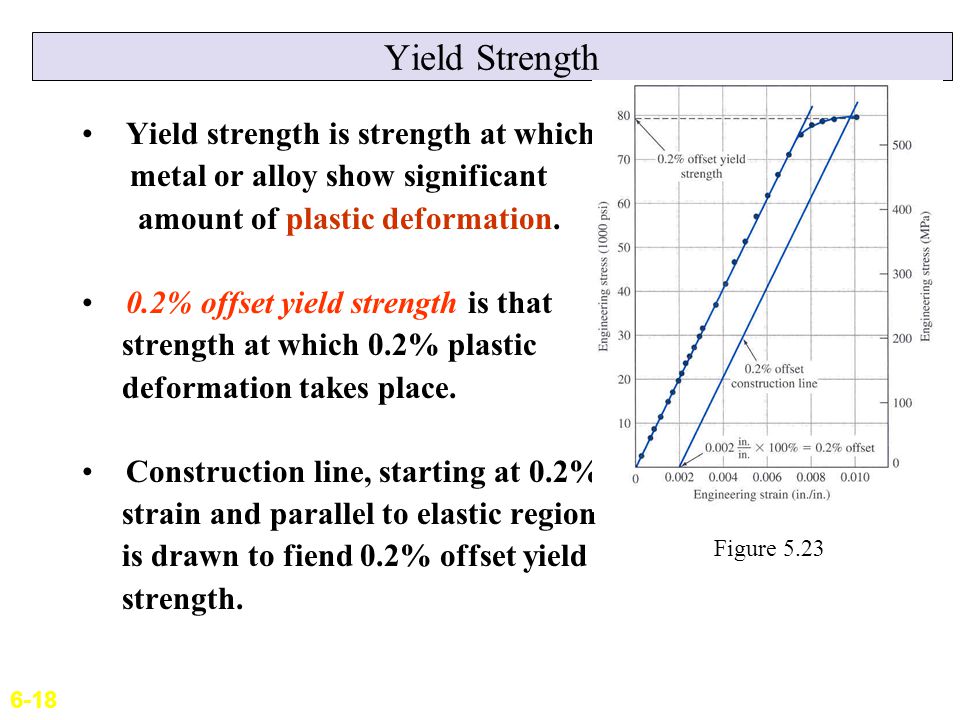
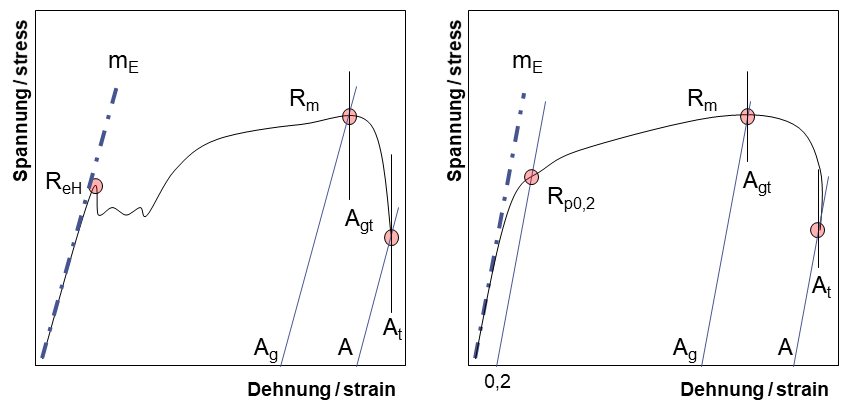
The yield strength is typically defined by the "02% offset strain" The yield strength at 02% offset is determined by finding the intersection of the stressstrain curve with a line parallel to the initial slope of the curve and which intercepts the abscissa at 02% The question, then, is "Is there an easy way to determine the 02% offset strain line, without a calculator handy?" Yes, there isThe calculation used for both continuous and discontinuous material was an offset yield of 02% strain Based on this calculation the stress values were determined for product verification For a continuously yielding material, it is recommended to use the offset yield calculationAn interception among the 02% offset line and the stress strain curve indicates the yield strength at 02% offset or 02% strain The yield strength which is an indication of the plastic deformation onset is known to be a significant factor in engineering structural or component designs where application of safety factors are common (equation 5)

Phy351 Ch 6
0.2 offset yield strength calculation
0.2 offset yield strength calculation-It is shown that the 02 pct offset yield strength of a material (in kg per sq mm) can be obtained from simple hardness measurements using the expression σ y = (H/3)(01) m2 , whereH is the Diamond pyramid hardness andm is Meyer's hardness coefficient This expression holds for brass, steel in either the cold rolled or tempered condition, and aluminum alloys in either the cold rolled orBy observation the offset yield strength (02% proof strength) can be seen to be around 80 MPa in this example (where the green line intersects the blue curve) Share Improve this answer


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library
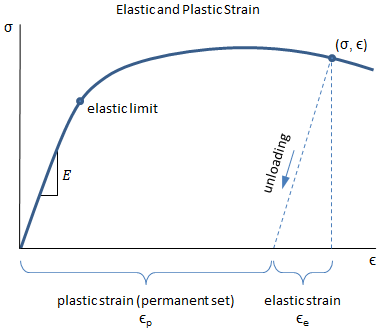
(b) Calculate the 02% offset yield stress in GPa for a cylindrical sample, whose stress strain curve is shown in this figure 300 00 103 psi MPa 0 1500 0 0008 1000 1000 100 100 0002 0000 0005 0010 0015 Strain 0040 Strain 0000 00 0060 0080 (c) For the same test, approximately, what is the tensile strength in MPa?The 02% yield strength or the 02% offset yield strength is calculated at 02% offset from the original crosssectional area of the sample (s=P/A) During yielding stage, the material deforms without an increase in applied load, but during the strain hardening stage, the material undergoes changes in its atomic and crystalline structureOffset yield strength determination requires a specimen that has been loaded to its 02% offset yield strength and unloaded so that it is 02% longer than before the test The offset yield strength is often referred to in Great Britain as the proof stress , where offset values are either 01 or 05%
When Viewing Any Engineering Stress Strain Curve, Where Is TheThe 02% offset yield strength (02% OYS, 02% proof stress, R P02, R P0,2) is defined as the amount of stress that will result in a plastic strain of 02% This is illustrated by the blue line in Figure 1 below This is the yield strength that is most often quoted by material suppliers and used by design engineers If aThe stress and strain in the sample are measured, recorded and plotted on a stressstrain graph A straight line offset at 02% strain is extended parallel to the linear portion of the graph until it meets the stressstrain curve The stress at the intersection between this line and the curve is the value of the proof stress Yield Strength
Offset yield strength is an arbitrary approximation of a material's elastic limitIt is the stress that corresponds to a point at the intersection of a stressstrain curve and a line which is parallel to a specified modulus of elasticity line This parallel line is horizontally offset by a predetermined amountThe 02 Percent Offset Rule The most common engineering approximation for yield stress is the 02 percent offset rule To apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×EThe stress corresponding to a specified permanent (plastic) deformation The specified permanent deformation has been standardized in the nonferrous industry as 02% offset on the stressstrain curve


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora
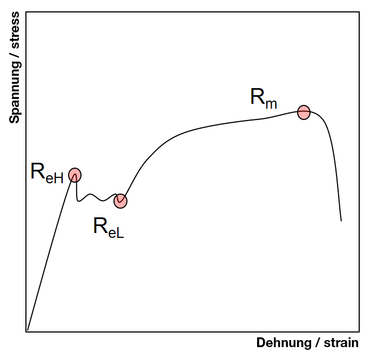
Line XB is offset a strain amount OX that is typically 02% of the gage length Point C represents the yield strength by extension under load (EUL) and is found by constructing a vertical line YC Line YC is offset a strain amount OY that is typically 05% of gage lengthThe tensile strength is calculated by dividing the maximum load by the original crosssectional area of the test specimen Yield Strength;About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve
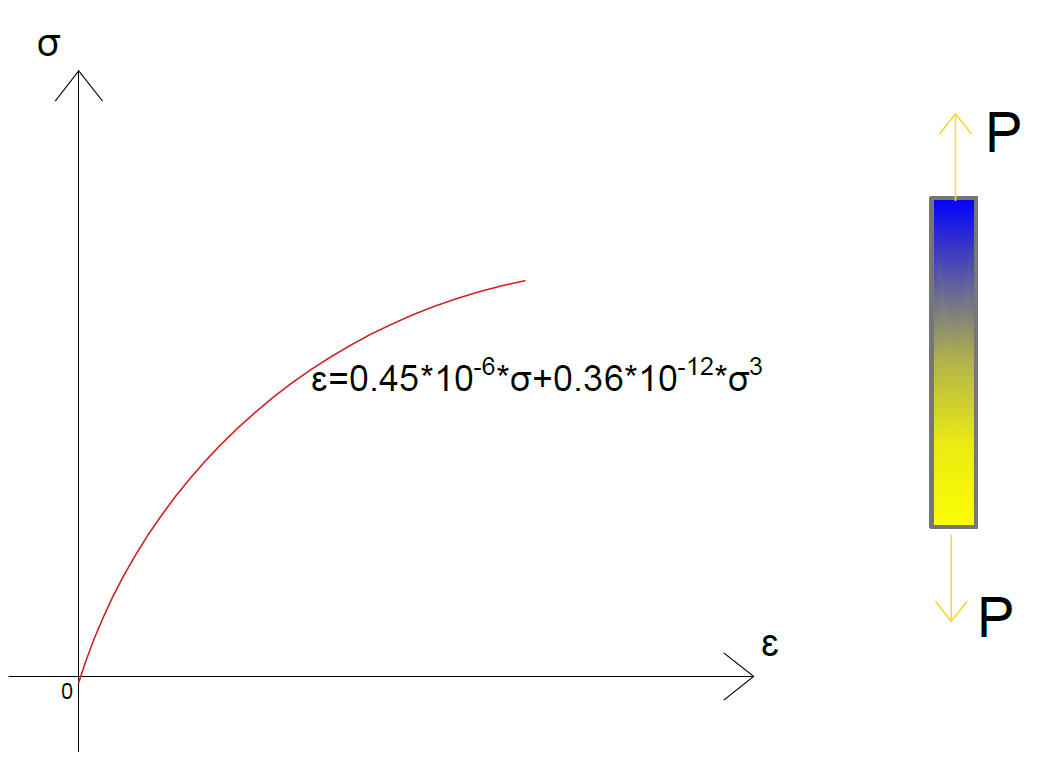


The Stress Strain Diagram For A Bone Is Shown And Can Be Described By The Equation Math Epsilon 0 45 Left 10 6 Right Sigma Math Math 0 36 Left 10 12 Right Sigma 3 Math Where Math Sigma Math Is In Kpa Determine The Yield
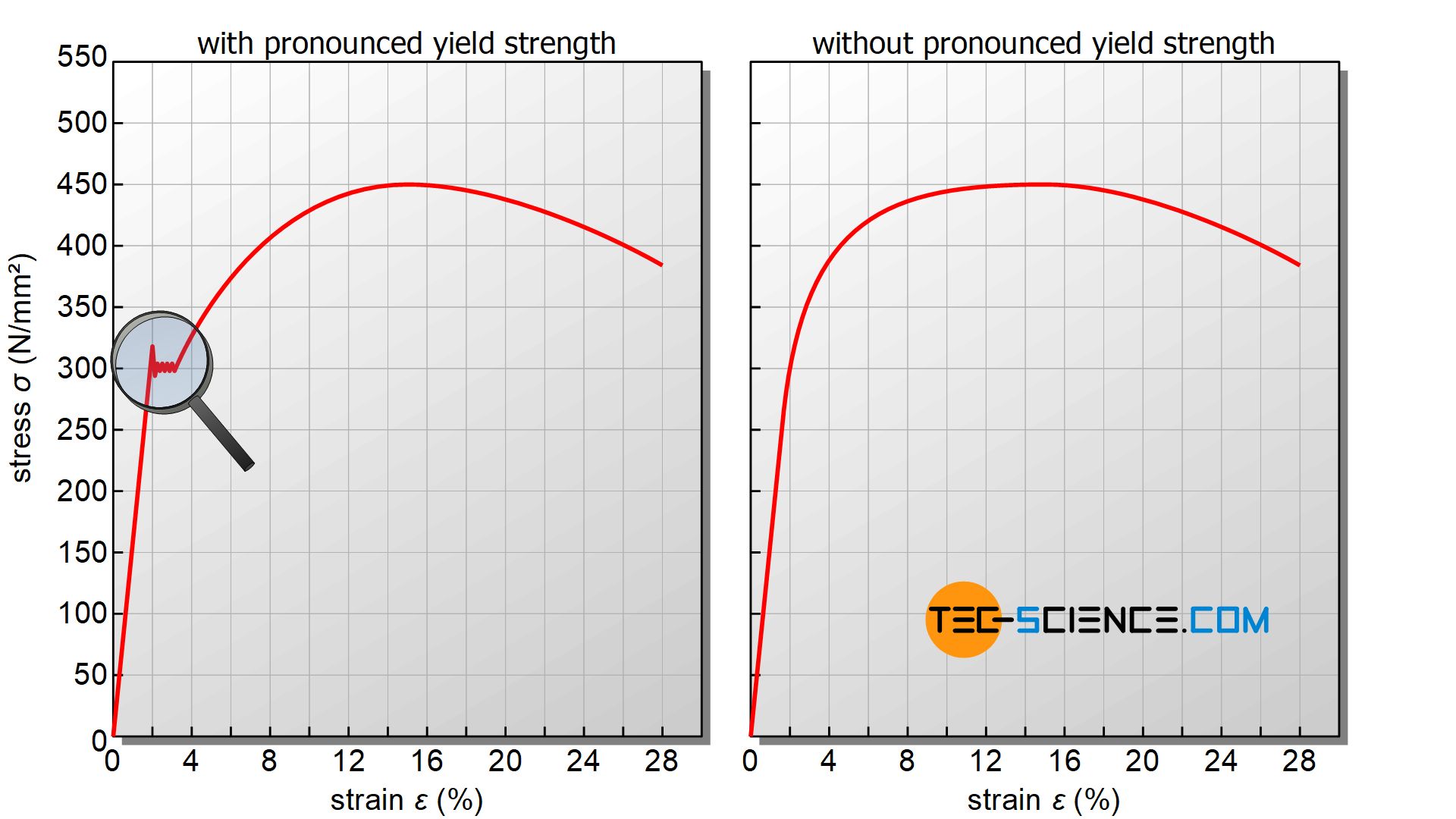
The yield strength is defined as the stress required to produce a small, amount of plastic deformation The offset yield strength is the stress corresponding to the intersection of the stressstrain curve and a line parallel to the elastic part of the curve offset by a specified strain (in the US the offset is typically 02% for metals and 2%The 02% offset method is the standard for finding the yield strength of materials Here's how we can take some Excel data and use the 02% offset in ExcelWhen a yield point is not easily defined on the basis of the shape of the stressstrain curve an offset yield point is arbitrarily defined The value for this is commonly set at 01% or 02% plastic strain 13


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd
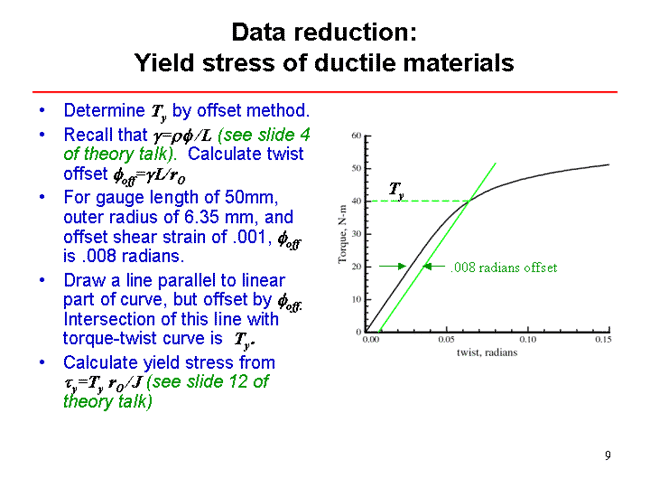


Aluminum Sample 9
The 02% yield number is meant to be the boundary of the material's linear elastic region I would say the material is well into the yield region by 1500 MPa, because there is significant (to the eye) plastic deformation occurring If you loaded the sample to 1500 MPa and then released, you would see permanent deformation after just one cycleQuestion (b)Show How To Determine The 02% Offset Yield Strength On The Plot Above And Show The Value You Determine Here (c) Show The Calculations To Determine The Ultimate Strength For This Material What Is Physically Occurring In The Specimen At The Ultimate Strength?Proof strength is therefore not a fixed material characteristic, such as the yield point, but will depend upon how much plastic deformation is specified It is essential therefore when considering proof strengths that the percentage figure is always quoted Most steel specifications use 02% deformation, R P02 in the EN specifications



Finding Minimum Difference Between Fit Line And Data Points In R Stack Overflow


Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 Bf Pdf
A good way of looking at offset yield strength is that after a specimen has been loaded to its 02 percent offset yield strength and then unloaded it will be 02 percent longer than before the test The offset yield strength is often referred to in Great Britain as the proof stress , where offset values are either 01 or 05 percentThe yield strength at 02% offset is determined by finding the intersection of the stressstrain curve with a line parallel to the initial slope of the curve and which intercepts the abscissa atLine XB is offset a strain amount OX that is typically 02% of the gage length Point C represents the yield strength by extension under load (EUL) and is found by constructing a vertical line YC Line YC is offset a strain amount OY that is typically 05% of gage length


Q Tbn And9gctox3cf4zpt H1tpvycayerw3xbv Ukqszfzrag5mxfqpo7il42 Usqp Cau



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic
The 02% yield strength or the 02% offset yield strength is calculated at 02% offset from the original crosssectional area of the sample During yielding stage, the material deforms without an increase in applied load, but during the strain hardening stage, the material undergoes changes in its atomic and crystalline structure , resulting inFor example, "Yield Strength (at 02% offset) = 51,0 psi" Young's Modulus of Common Engineering Materials Some examples of yield strength for metals are as follows Typical StressStrain Curve Plastics Alternate values are sometimes used instead of yield strength Several of these are briefly described belowDepending on the material's stressstrain behavior at yield, a preferred yield calculation is specified by the chosen standard For instance, metals test standards ( ASTM E8 or ISO 62 ) have standardized a 02% offset yield , which allows the metals industry to objectively evaluate different metals against each other



Phy351 Ch 6


Http Web Ncyu Edu Tw Lanjc Lesson C3 Class Chap02 A Pdf
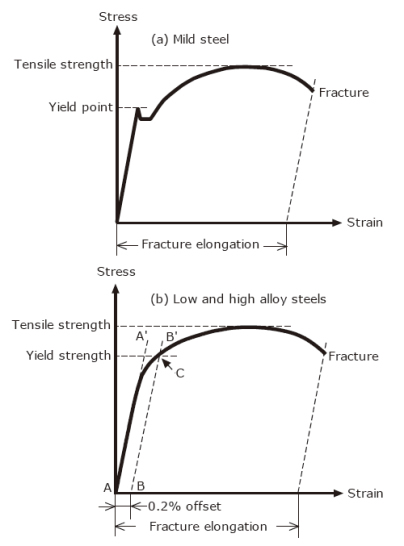
This paper presents computer procedures for the calculation of offset yield strength (Sy) and for the evaluation of the uncertainty in its computation (typ ical ly 01 % or 02 % for metal sThe 02% strain offset approach is mostly used to calculate the yield stress and serves as an efficient method for crosslab comparisons of measured material properties However, it is difficult to accurately determine the yield of the bone Especially when computational models require accurate material parameters, clarification of the yield point is neededDefinable yield point, gradual transition from linear to nonlinear region, yield stress always determined by offset method, in general, use 02% offset, it should be referred as offset yield stress, it is slightly above the proportional limit The ductility of material in tension can be characterized by its elongation and by the reduction area
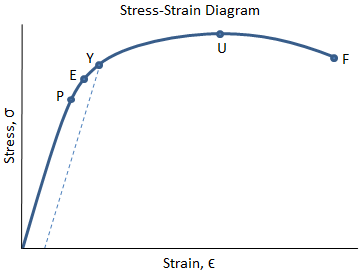


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress
A video of a tensile test of steel is available here https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=sQkI_Nj1AxsA video demonstrating how to calculate proof stress is availNow I need to get the 02% (strain) offset in order to get my yield stress View Why is the yield strength calculated on the basis of 02% or 05% strain only?By observation the offset yield strength (02% proof strength) can be seen to be around 80 MPa in this example (where the green line intersects the blue curve) Share Improve this answer
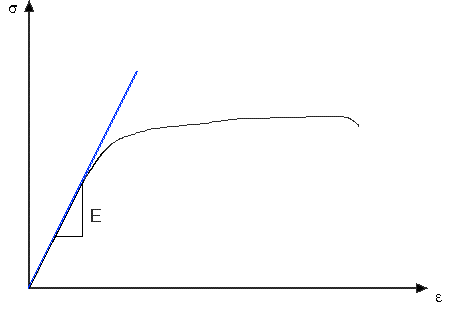


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics



Determining 0 2 Offset Yield Stress Capstone Video Library Pasco
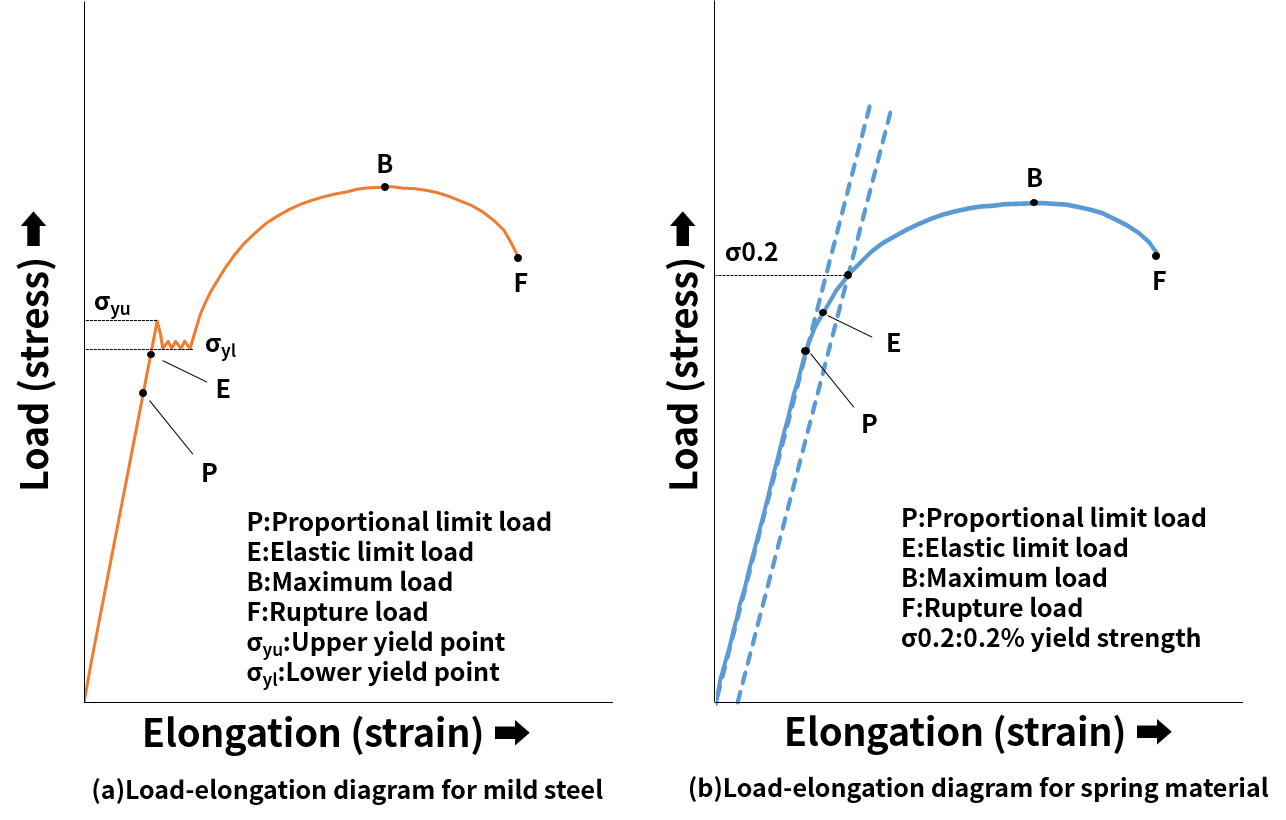
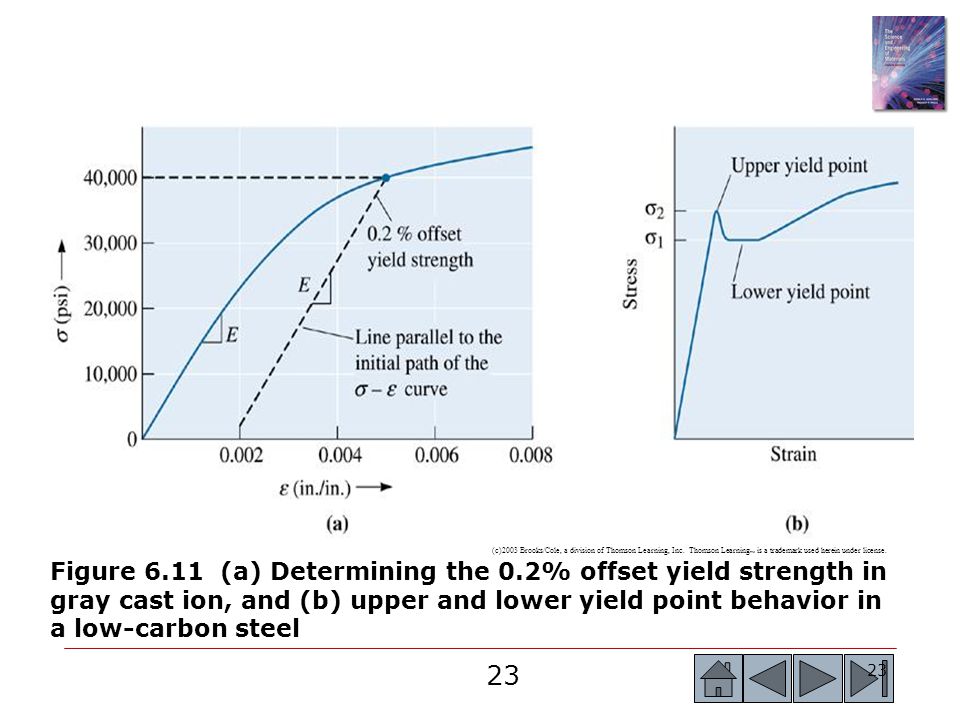
Once you have determined the Young's Modulus for the experimental run, you can then enter this data into the calculator to set the slope of the 02% offset line Next, you can use the Smart Tool to find the value of the coordinate of the experimental stressYIELD STRENGTH (02% OFFSET) YIELD STRENGTH (005% OFFSET) EL ROCKWELL HARDNESS VICKENS HARD BRINELL HARD SHEAR STRENGTH FATIGUE STRENGTH* IZOD IMPACT STRENGTH in % F ksi ksi ksi ksi % BC F30T 500 3000 ksi ksi ftlb mm C MPa MPa MPa MPa MPa MPa J M01 00 0 TYP 68 95 48 180 1 00 655 331 180 160 1 In determining Cu min, Cu mayDifferent values may be obtained if tangents are drawn at different points Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield point



After Fracture The Total Length Was 47 42 Mm And The Diameter Was 18 35 Mm Plot The Engineering Brainly Com
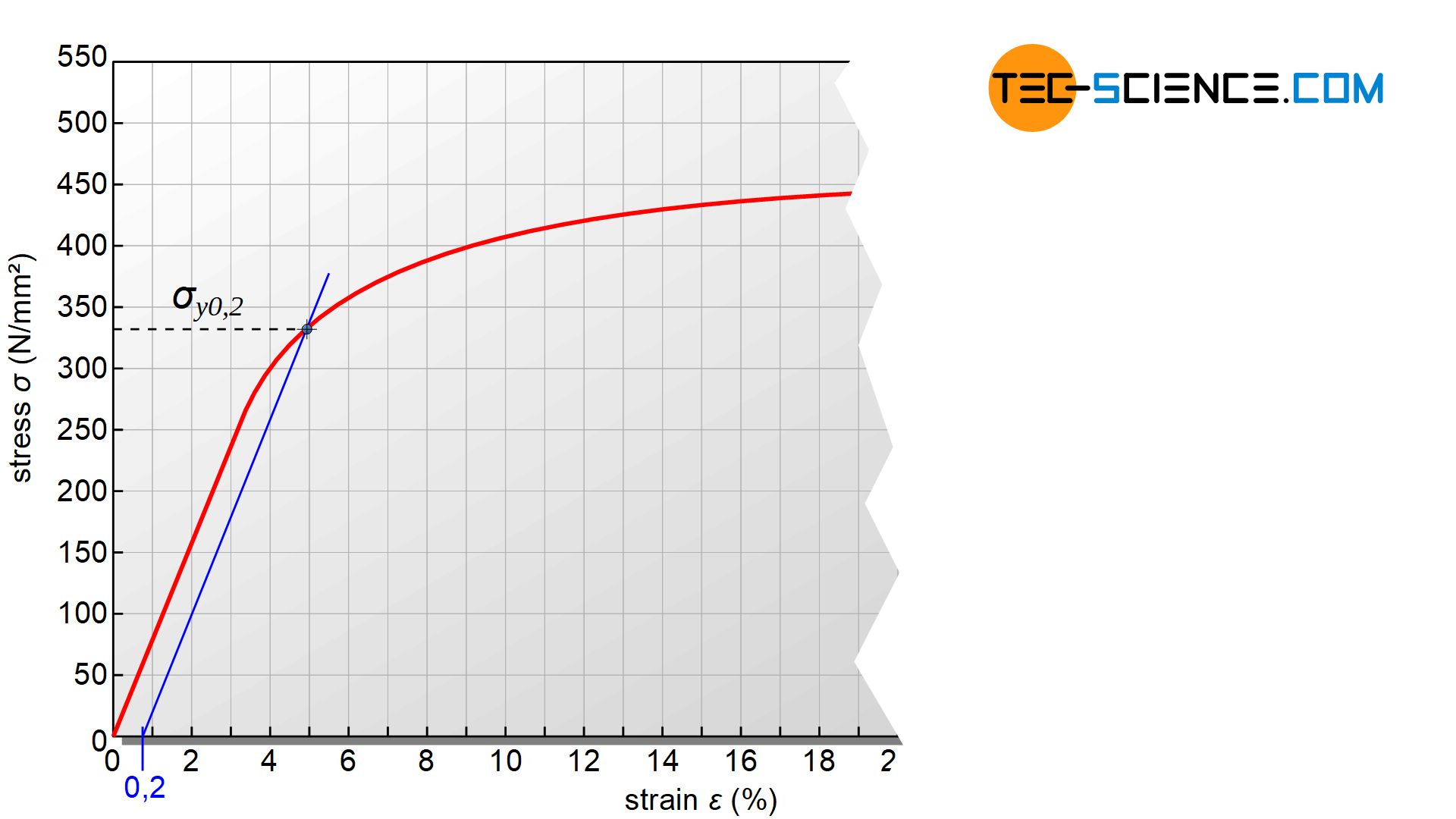


Gvvy2hhnalj6dm
Offset yield strength is an arbitrary approximation of a material's elastic limitIt is the stress that corresponds to a point at the intersection of a stressstrain curve and a line which is parallel to a specified modulus of elasticity line This parallel line is horizontally offset by a predetermined amountThe yield strength of 02% is offset, for example, by drawing through the point of the horizontal axis abscissa No 02% (or 0002), the line parallel to the initial straight part of the voltage chart Stress corresponding to the point in this result is defined as a yield strength of 02% compensatedAt the yield point, the force becomes strong enough that the steel will stretch and not return to its original shape This amount of force is the yield strength To test yield strength in our example, you would put our ½13 bolt into the tensile machine, stretch the part until it distends, and calculate the force at the point of yield



What Is The Difference Between 0 2 Yield Stress And Yield Stress In Aluminum Quora



How To Draw A Line Parallel To The Linear Portion Of The Curve In Excel Stack Overflow
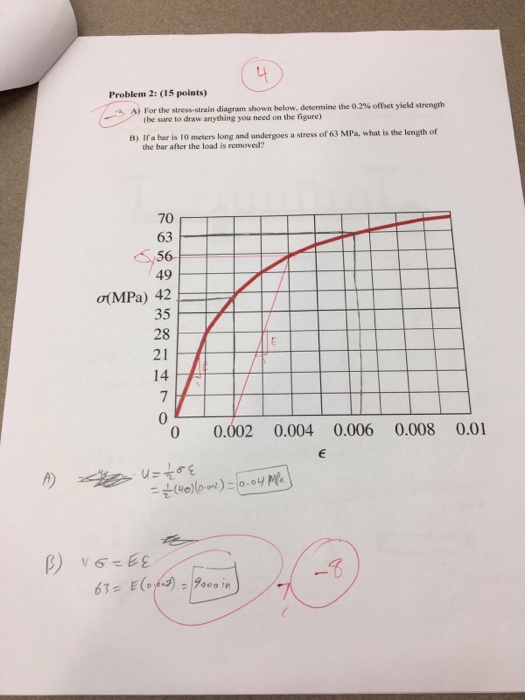
How do I determine the 02% offset yield strength using the MTS and PASCO Capstone?Well the conversion from elasticity to plasticity can be very subtle for many materials so it might not be always very easy to figure out the yield point, that is the point on the stressstrain curve, where elasticity changes to plasticity In othQuestion 5 Determine The 02% Offset Yield Strength, The Percent Elongation And The Tensile Question Question 5 Determine The 02% Offset Yield Strength, The Percent Elongation And The Tensile Strength For The Specimen With The Dimensions Given Below In Mm 240 2 0,32 0 180 假) 140 1 160 70 1개) 100 80 60 40 100 0 21 00 0103 04



A Simple Method For Measuring Plastic Properties Of Power Hardening Metals Via The Indentation Curve With A Large Depth


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf
The 02% offset yield strength (02% OYS, 02% proof stress, R P02, R P0,2) is defined as the amount of stress that will result in a plastic strain of 02% This is illustrated by the blue line in Figure 1 below This is the yield strength that is most often quoted by material suppliers and used by design engineers If aSpecifically, the yield point is where the stressstrain curve has a 02% offset from the Young's modulus Engineers use this 02% offset to have an easilyidentifiable point on the stressstrain curveDifferent values may be obtained if tangents are drawn at different points Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield point
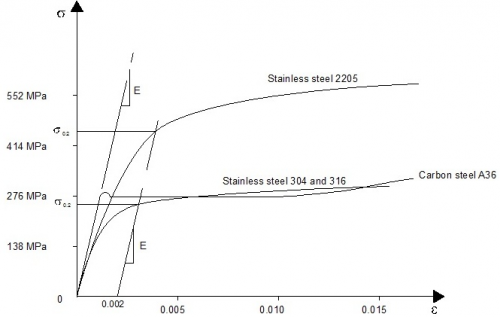


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info


Q Tbn And9gcrhvogkniaf5aix Yv5viz777uqklm0zjg52gijgphwvl7khodo Usqp Cau
Then on the stressstrain diagram, lay off om equal to the specified value of the offset (ie yield strength ~02%), draw mn parallel to OA, and thus locate r, the intersection of mn with the stressstrain curve corresponding to load R, which is the yield strength load In recording values of yield strength obtained by this method, the valueThe stressstrain diagram for a steel rod is shown and can be described by the equation ε=0(1e06)σ0(1e12)σ 3 where s in kPa Determine the yield strength assuming a 05% offsetFor example, "Yield Strength (at 02% offset) = 51,0 psi" Young's Modulus of Common Engineering Materials Some examples of yield strength for metals are as follows Typical StressStrain Curve Plastics Alternate values are sometimes used instead of yield strength Several of these are briefly described below



Mechanical Testing Tensile Testing Part 1 Twi


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
RambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based onHardening behavior and yield offset In the last form of the Ramberg–Osgood model, the hardening behavior of the material depends on the material constants and Due to the powerlaw relationship between stress and plastic strain, the Ramberg–Osgood model implies that plastic strain is present even for very low levels of stress Nevertheless, for low applied stresses and for the commonlyRambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
The ultimate strength design method is similar to LRFD There is a nominal strength that is reduced by a factor which must exceed the factored design stress For beams, the concrete only works in compression over a rectangular "stress" block above the na from elastic calculation, and the steel is exposed and reaches the yield stress, F y



What Is Tensile Testing Instron


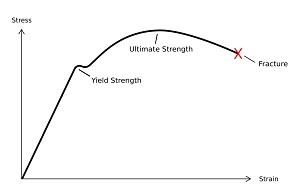
Engineering Stress Strain Curve



How To Determine The Yield Strength Of Brass Quora


Http Maecourses Ucsd Edu Jmckittr Mae Wi11 Assignment 5 solutions Pdf
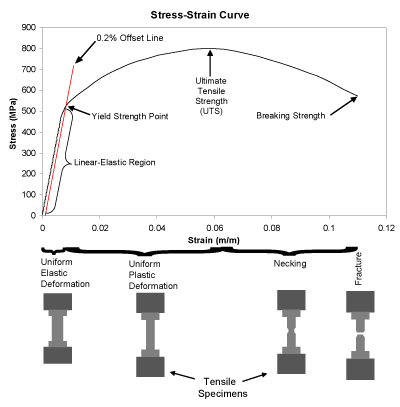


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials
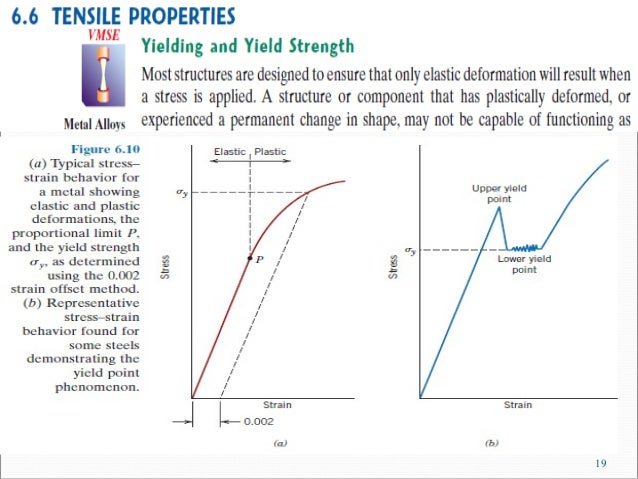


Lec 2 Stress Strain Diagram Lec 2
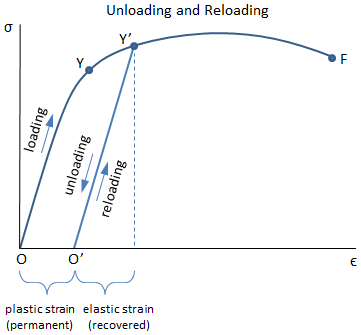


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Solved The Stress Strain Diagram For A Bone Is Shown And Can Be Described 1 Answer Transtutors
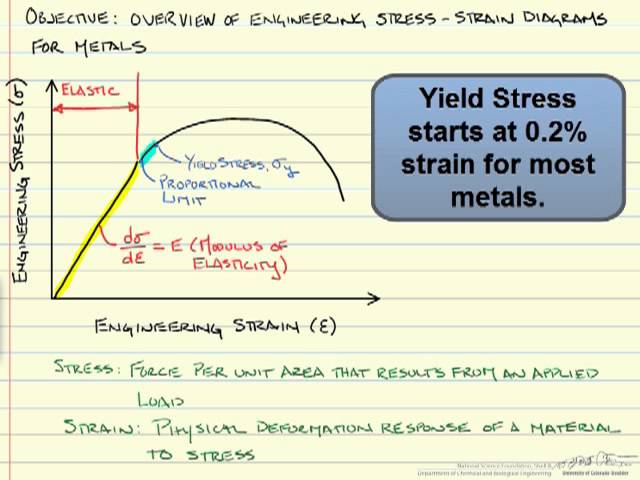


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Properties Of Metals Engineering Library



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube



Solved B Calculate The 0 2 Offset Yield Stress In Gpa Chegg Com



Proportional Limit An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
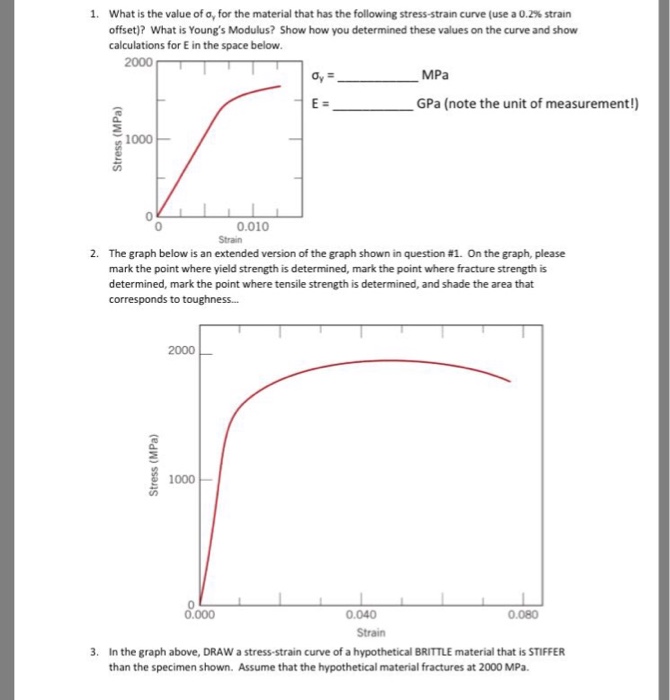


Solved 1 What Is The Value Of O For The Material That H Chegg Com


People Engr Ncsu Edu Ytzhu Class Teaching Mse0 Lecture7 Sept16s Pdf
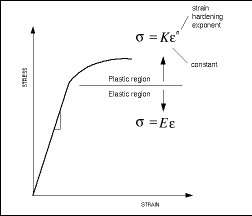


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf
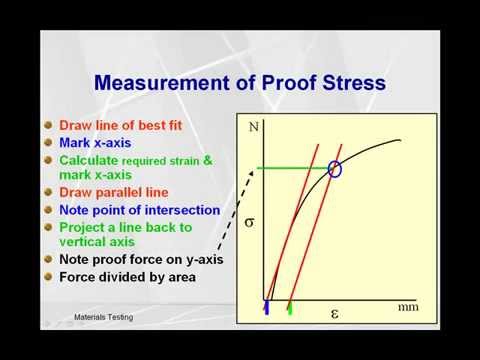


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube



Stress Strain Diagrams Showing Methods Of Yield Strength Determination Download Scientific Diagram



What Is 0 2 Proof Stress Of Steel Quora



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



A Simple Method For Measuring Plastic Properties Of Power Hardening Metals Via The Indentation Curve With A Large Depth


Http Www Schooloftesting Com Download How To Interpret Stress Strain Diagrams How to interpret stress Strain diagrams Pdf


Yield Point Yield Point Ratio Offset Yield Zwickroell



Determining 0 2 Offset Yield Stress Capstone Video Library Pasco



Determining Tensile Yield Stresses From Small Punch Tests A Numerical Based Scheme Sciencedirect


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Offset Yield Strength Instron


Mechanical Properties Of Metals I Ppt Download


Solved For The Stress Strain Diagram Shown Below Determi Chegg Com



Mechanics Of Materials 0 2 Percent Offset Method And Percent Elongation Notes Youtube


Yield Point Yield Point Ratio Offset Yield Zwickroell


Yield Strength Testing Yield Strength Ultimate Strength Breaking Strength


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau


What Is 0 2 Of Offset Method In Yield Strength Quora


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Mechanical Testing Tensile Testing Part 1 Twi



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials


Chapter 6 Mechanical Properties And Behavior Ppt Download


Gvvy2hhnalj6dm



Materials Testing Glossary Admet
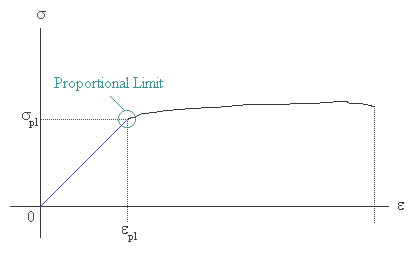


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics
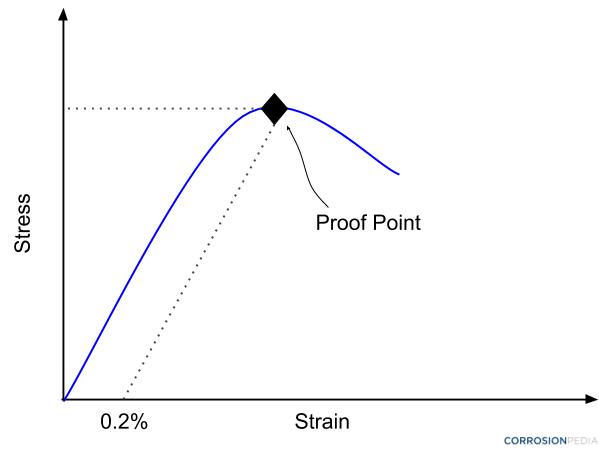


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet


Determining 0 2 Offset Yield Stress Capstone Video Library Pasco
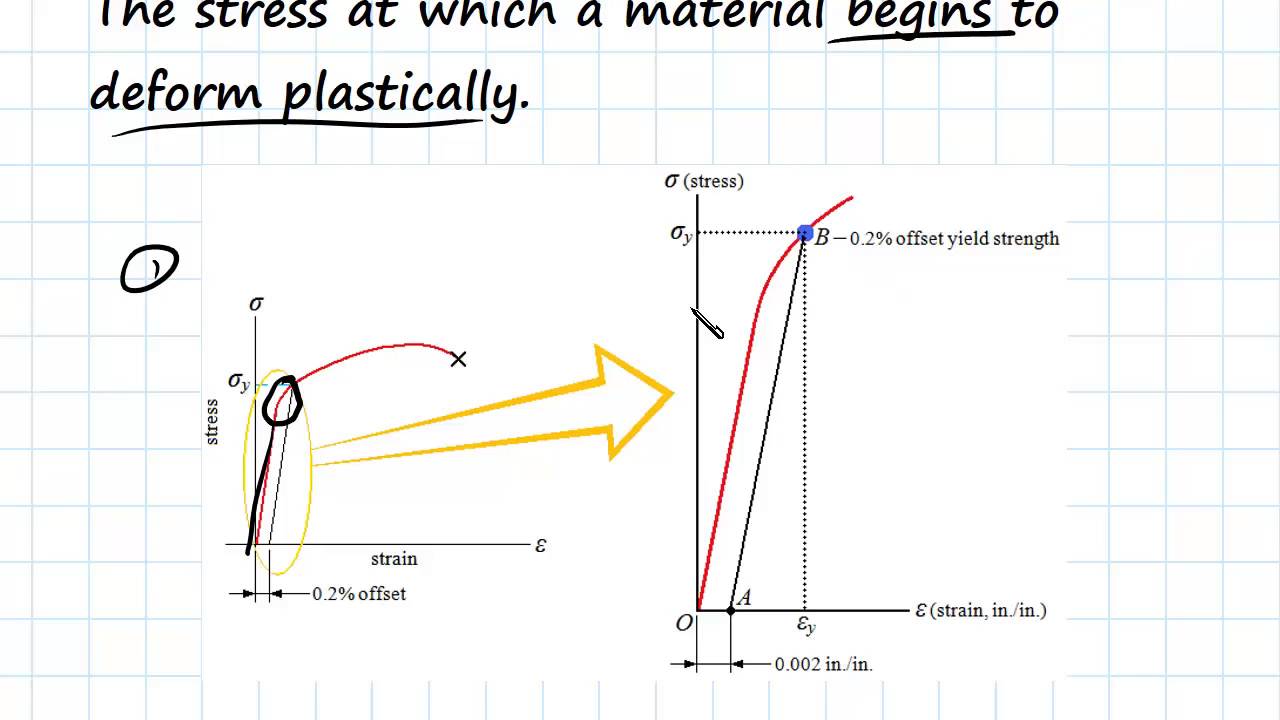


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube
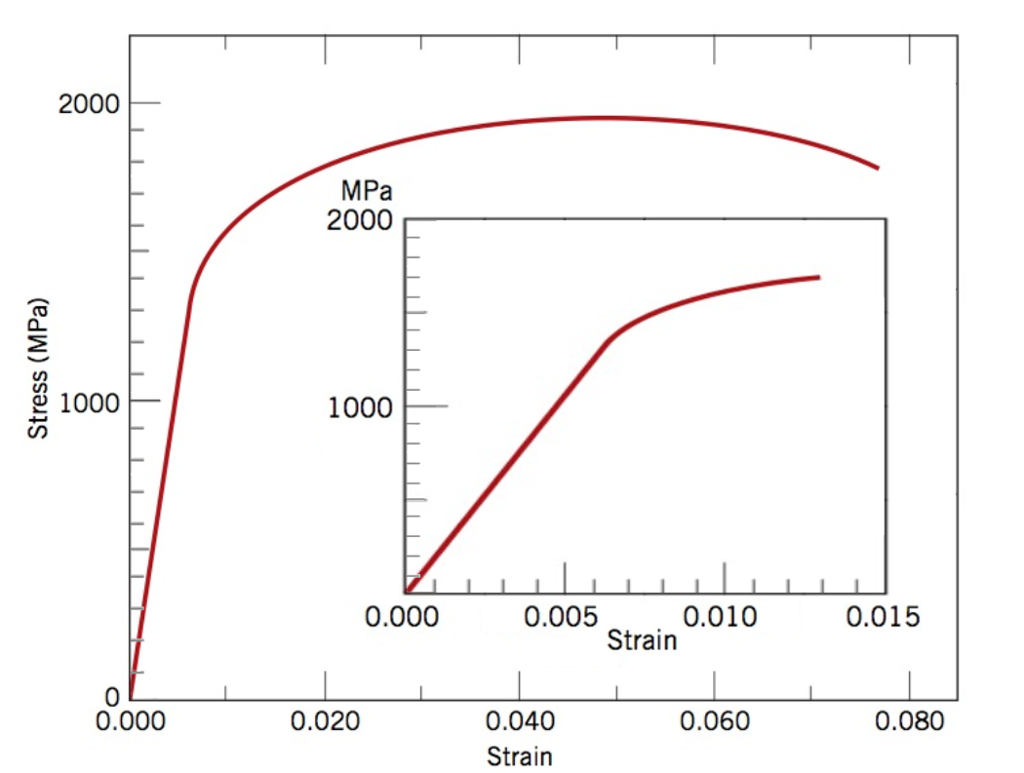


Solved A Using The 0 2 Strain 0 002 Strain Offset Met Chegg Com


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve
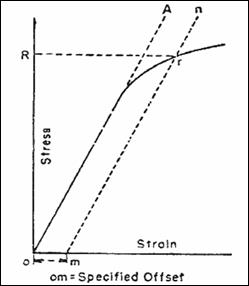


To Determine Yield Strength Tensile Strength Of A Steel Bar By Offset Secant Method



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article


Civl 1101



Yield Stress And Strain Calculations Based On 0 2 Offset Method Of Download Table



How To Draw 0 2 Offset Line On A Stress Strain Graph Youtube
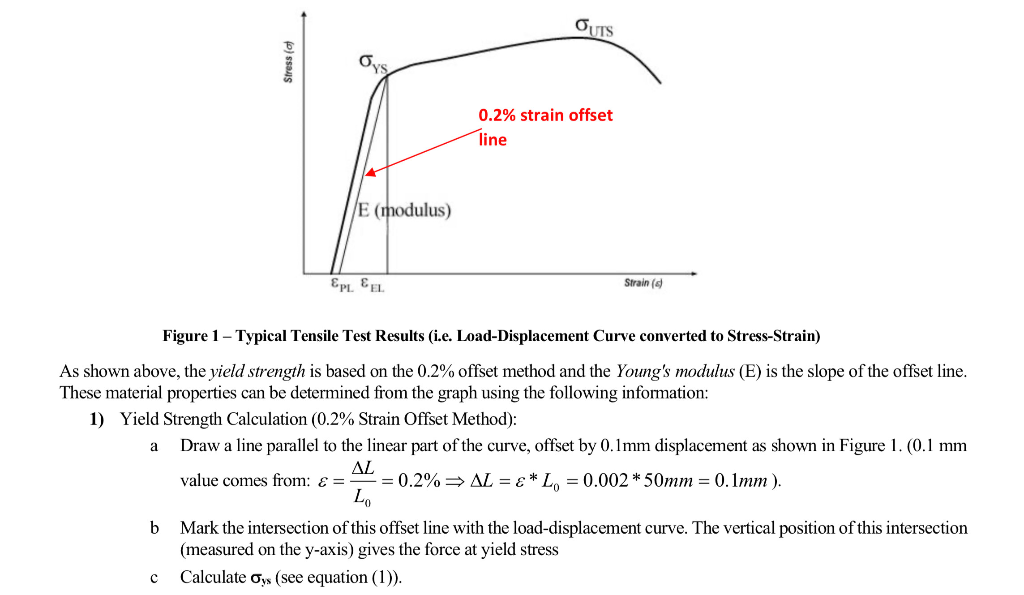


Solved Tensile Testing Machine Is A Load Versus Displacem Chegg Com



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
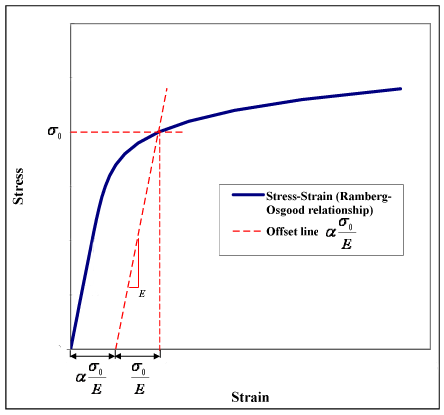


Ramberg Osgood Relationship Wikipedia



How To Calculate Yield Point At 0 2 In Stress Strain Curve Quora
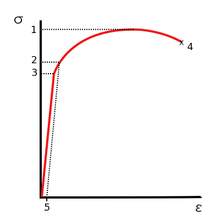


Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia
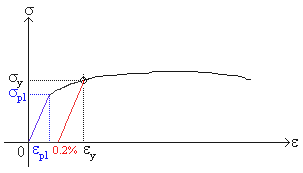


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


Http Www Ni Com Pdf Academic Us Me105 Lab3 03 Pdf



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


Stress Versus Strain
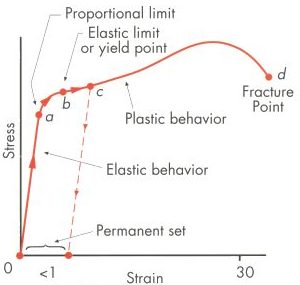


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Texture Analysis Professionals Blog Tensile Testing Using A Texture Analyser Calculating Fundamental Parameters
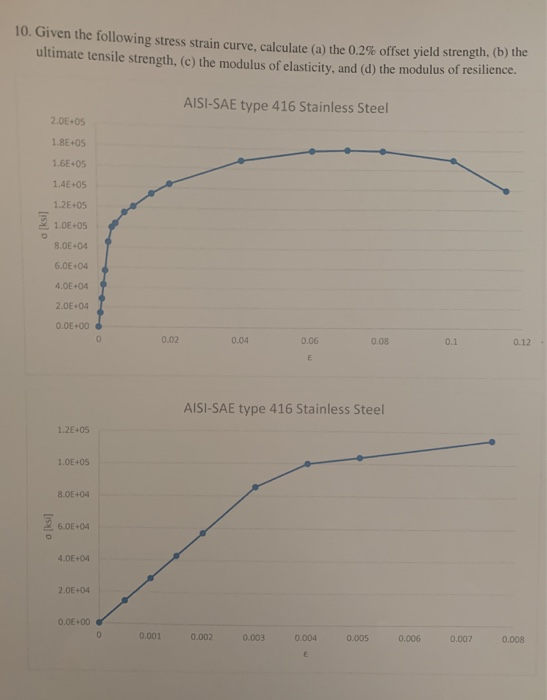


Solved 10 Given The Following Stress Strain Curve Calcu Chegg Com


Http Www Iitk Ac In Mme Test Mme310 Pdf
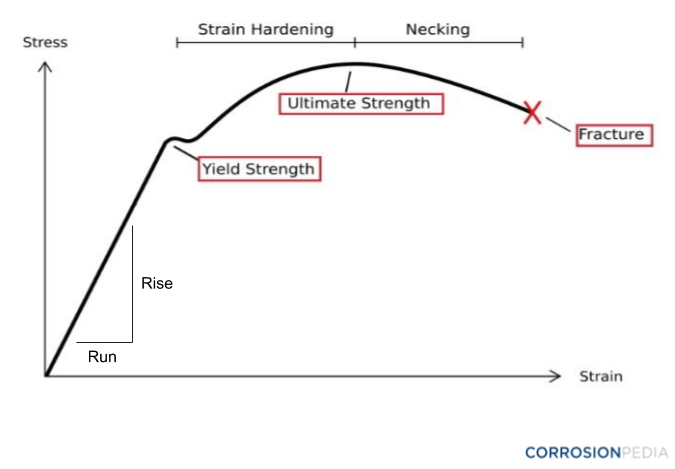


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Tensile Testing Data Sheet Please Fill In Your Name Group Members Data And Instructor S Name Mark Gage Length Indents Using The Hammer Measure The Ppt Download


How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs
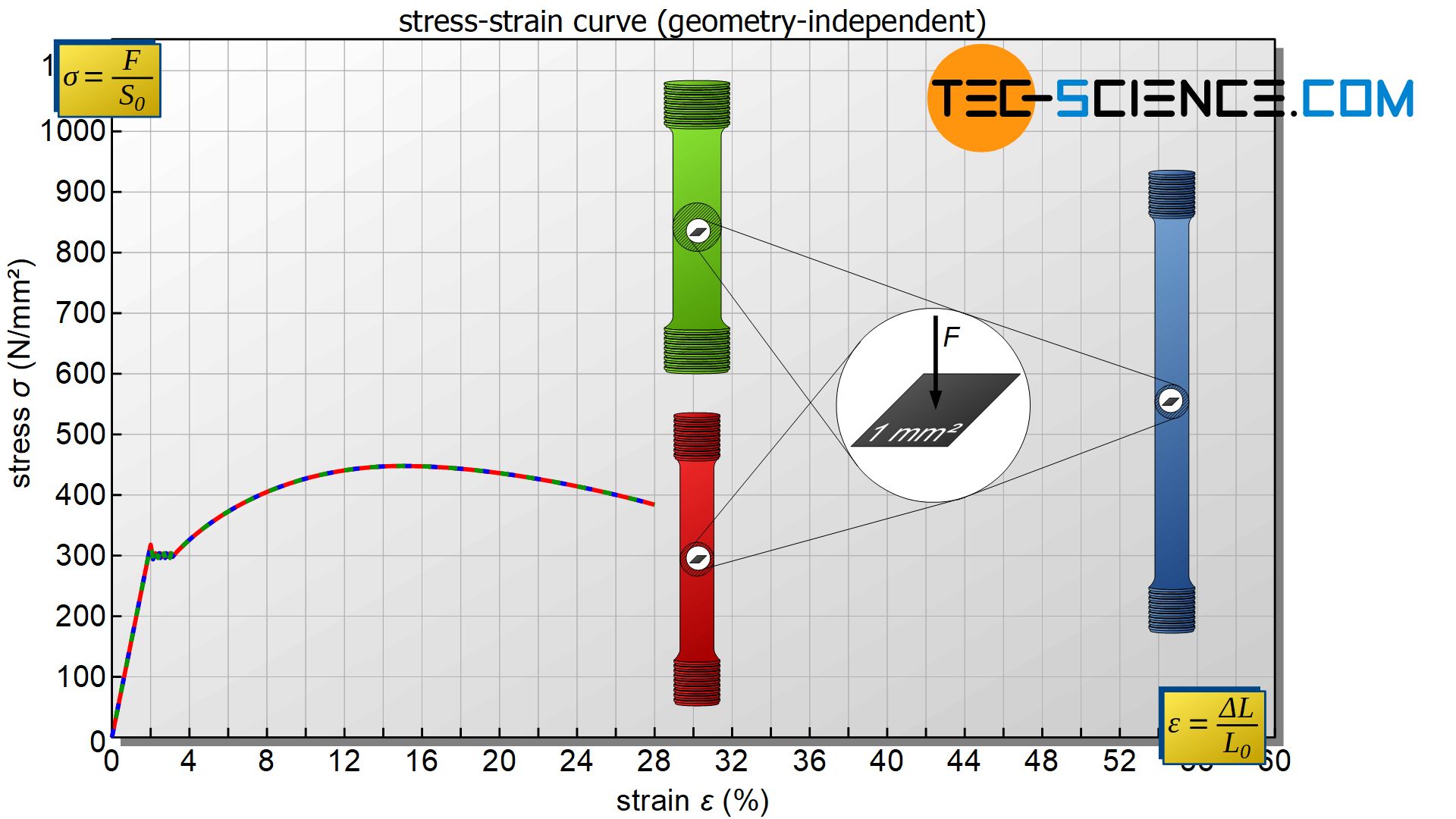


Gvvy2hhnalj6dm



Elastic Range An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
コメント
コメントを投稿